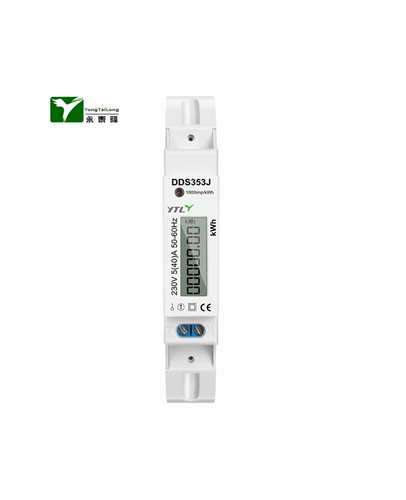
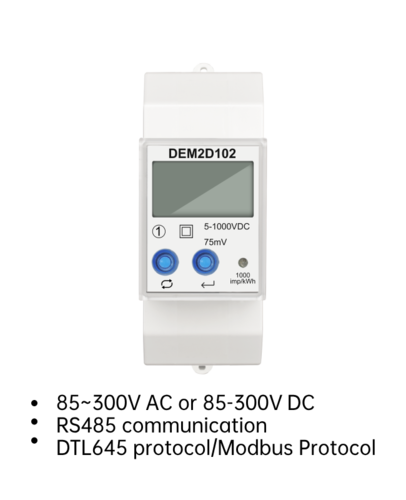
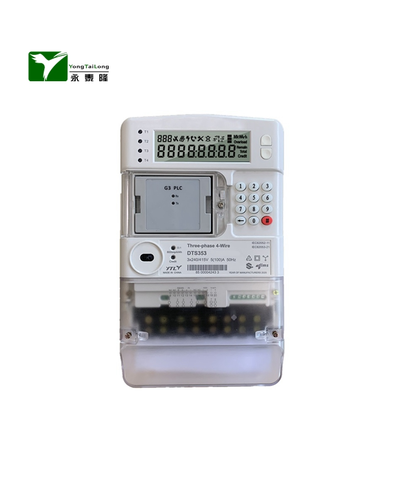
 A prepaid energy meter, also known as a prepayment meter or pay-as-you-go meter, is a type of electricity meter that allows consumers to pay for their energy usage in advance. Unlike traditional postpaid meters, which require consumers to pay for their electricity after they have used it, prepaid energy meter require consumers to purchase credit before they can use electricity. The credit is then deducted as the consumer uses electricity. When the credit runs out, the electricity supply is automatically disconnected until more credit is purchased.
A prepaid energy meter, also known as a prepayment meter or pay-as-you-go meter, is a type of electricity meter that allows consumers to pay for their energy usage in advance. Unlike traditional postpaid meters, which require consumers to pay for their electricity after they have used it, prepaid energy meter require consumers to purchase credit before they can use electricity. The credit is then deducted as the consumer uses electricity. When the credit runs out, the electricity supply is automatically disconnected until more credit is purchased.
Prepaid energy meter is becoming increasingly popular in many parts of the world, particularly in developing countries. They are seen as a way to improve energy access for low-income households and reduce electricity theft and non-payment. In addition to the benefits for consumers, prepaid energy meter also offer advantages for energy providers. They can help reduce the costs and risks associated with billing and collection.
Prepaid energy meter is typically equipped with a digital display that shows the amount of credit remaining, as well as the amount of electricity being used. Consumers can purchase credit for their meters through a variety of methods, including mobile payment services, bank transfers, and retail outlets. Some prepaid energy meter also support remote top-up, allowing consumers to add credit to their meters without having to physically access the meter.
One of the main advantages of prepaid energy meter is that they give consumers greater control over their energy usage and spending. By allowing consumers to monitor their electricity usage in real-time and adjust their consumption accordingly, prepaid energy meter can help promote energy efficiency and reduce wastage. In addition, prepaid energy meter can also help consumers to budget for their energy expenses more effectively. This is because they can purchase credit in smaller, more manageable amounts.
Another advantage of prepaid energy meter is that they can help to reduce electricity theft and non-payment. Because consumers must pay for their electricity in advance, there is less incentive for them to tamper with their meters or avoid paying for their electricity. This can help improve the financial sustainability of energy providers and ensure that they can continue to invest in expanding and improving the electricity supply.
Despite their numerous advantages, prepaid energy meter also has some drawbacks. For example, some critics argue that prepaid energy meter can be a burden for low-income households, as they may struggle to afford the upfront cost of purchasing credit. In addition, there are concerns that prepaid energy meter may be used as a tool for disconnection and disempowerment, particularly in cases where consumers are unable to afford to top up their meters.
In conclusion, prepaid energy meter is a type of electricity meter that allows consumers to pay for their energy usage in advance. They offer numerous advantages, including greater control over energy usage and spending, as well as reduced electricity theft and non-payment. However, they also have some drawbacks, and it is important to carefully consider the potential implications of their widespread adoption.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体


.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)










