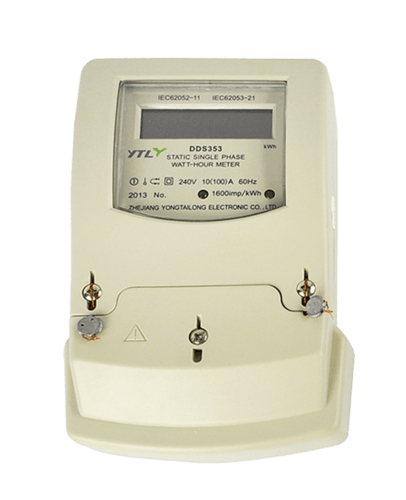
Whole current meters , as know as total current meter, which is an instrument that measures the total current flowing. A whole current refers to the current passing through a certain cross section of space, including conduction current, displacement current, and convection current. That is, the sum of conduction current (Ic), convection current (Iv), and displacement current (Id) equals full current. Among them: Ic refers to the current formed by the directed movement of free charges within the conductor, Iv refers to the current formed by the directed movement of free charges outside the conductor, and Id refers to the equivalent current of the changing electric field.
The total current law, also known as Kirchhoff's law or Kirchhoff's current law, is one of the fundamental laws in circuits. It states that at a junction in an electrical circuit, the sum of currents flowing into the junction is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of the junction. The total current law is an essential foundation for circuit analysis and can be utilized to resolve various circuit issues.
The total current is continuous and forms a closed circuit in space. Total current is a fundamental principle of electrodynamics, and the magnitude of the current is equal to the voltage in the circuit divided by the total resistance in the circuit. Based on this principle, it can be used to analyze the relationship between voltage and resistance in a circuit. whole current meters are also designed based on this principle.
In addition to measuring voltage, current, power, and electricity in the circuit, whole current meters also have many extended functions added based on market demands and user needs. These include remote communication, event alarms, load profile, load control, anti-tamper electricity, prepaid electricity, etc.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体





-1.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)