A prepayment electricity meter, also known as a prepaid electricity meter, is a type of electricity meter that allows customers to pay for their electricity usage before consuming it. Here's how it works:
How it works:
1. The customer purchases a prepayment electricity card or token, which is loaded with a specific amount of electricity units.
2. The customer inserts the card or token into the meter, and the meter displays the available balance.
3. When the customer uses electricity, the meter automatically deducts the consumed units from the available balance.
4. If the balance reaches zero, the electricity supply is interrupted until the customer recharges the meter with more units.
Benefits:
1. Cost control: Prepayment meters help customers manage their electricity consumption and budget better, as they can see their usage in real-time.
2. Reduced debt: By paying for electricity in advance, customers are less likely to accumulate debt or owe money to their utility company.
3. Increased payment discipline: Prepayment meters encourage customers to be more mindful of their energy consumption and reduce wastage.
4. Reduced disputes: With a prepayment system, there are fewer disputes over bills and payments, as customers are aware of their exact usage and payment status.
Types of prepayment systems:
1. Card-based systems: Customers purchase cards or tokens with a specific amount of credit, which are inserted into the meter.
2. Token-based systems: Customers purchase tokens that are inserted into the meter to recharge their account.
3. Mobile-based systems: Customers use their mobile phones to recharge their accounts remotely using mobile apps or SMS.
Challenges and limitations:
1. Limited payment options: Some prepayment systems may not offer flexible payment options, such as online banking or credit card payments.
2. Inconvenience: Customers may need to physically visit a vendor or retailer to purchase prepaid cards or tokens.
3. Limited access: Prepayment meters may not be suitable for customers who have limited mobility or access to vendors.
4. Technical issues: Prepayment meters can malfunction or require frequent maintenance, leading to disruptions in service.
Conclusion:
Prepayment electricity meters can be an effective way for customers to manage their energy consumption and reduce debt. However, it's essential to consider the challenges and limitations associated with these systems to ensure they are implemented and used effectively.
| Type | Communication | CIU Communication | Function |
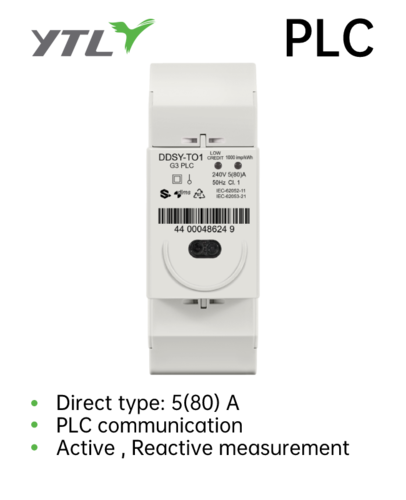
| K212-01-PLC | PLC | / | Active , Reactive measurement |
| K212-02-PLC | PLC | / | Build in Rely, Shunt sampling |
| K212-03-PLC | PLC | / | Build in Rely, Shunt sampling,Neutral measurement |
| K212-04-PLC | PLC | / | Build in Rely, Shunt sampling,Neutral measurement,Tariff,Event alarm |
| K212-05-PLC | PLC | PLC/Bluetooth | Build in Rely, Shunt sampling, |
| Neutral measurement,Tariff,Event alarm | |||
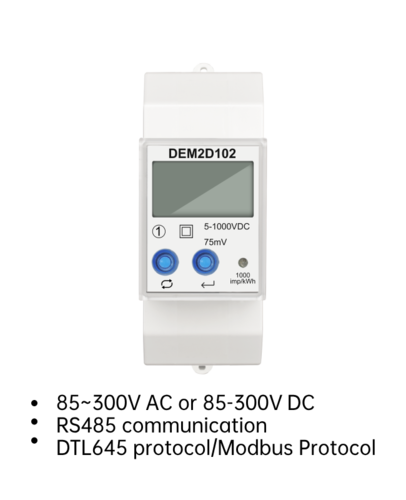
| K212-06-RS485 | RS485 | / | Active , Reactive measurement |
| K212-07-RS485 | RS485 | / | Build in Rely, Shunt sampling,Neutral measurement,Tariff,Event alarm |
| K212-08-Wifine | Wifine | Twisted Pair wire/RS485/RF | Different measurements way,Neutral measurement,Event alarm |
| K212-09-Wifine | Wifine | Bluetooth | Different measurements way,Neutral measurement,Event alarm |
| K212-10-Wifine | Wifine | Wifine/Bluetooth | Different measurements way,Neutral measurement,Event alarm |
| K212-11-Wifine | Wifine | Bluetooth | Build in Rely, Event alarm |

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体









.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)



