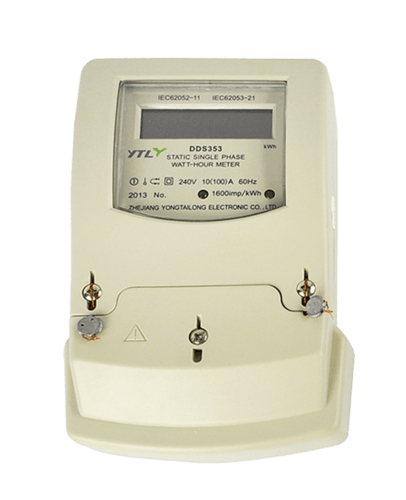
A 2-wire energy meter, also known as a two-wire meter, is a common device for measuring electrical energy, particularly suitable for measuring small power appliances such as light sources and personal household appliances. The following is a detailed analysis of the 2-wire energy meter, aimed at helping readers fully understand its working principle, characteristics, applications, and precautions.

1. Working principle
The working principle of a 2-wire energy meter is based on the fundamental Ohm's law and the power calculation formula, which states that energy consumption equals the product of voltage and current (p = ui). In a 2-wire system, the two wires serve both as power lines and signal lines, achieving the dual function of communication and power supply. This design simplifies the wiring process, reduces construction and cable costs, and brings great convenience to on-site construction and later maintenance.
Specifically, when current flows through the load of a two-wire energy meter, the internal metering chip of the meter captures the changes in voltage and current, and calculates the energy consumption based on this. This process is continuous, allowing the meter to record and display energy consumption in real time.
2. Characteristics
a. Simple wiring: The 2-wire energy meter has only two connection terminals, used to connect the power supply and the load, without the need for a neutral wire, simplifying the circuit structure.
b. Low cost: Due to the simple wiring, the production and installation costs of two-wire energy meters are relatively low, making them more affordable.
c. Easy to maintain: The maintenance of secondary energy meters is relatively simple due to their straightforward circuit structure, making it easy to troubleshoot and repair when faults occur.
d. Limited accuracy and measurement range: The design of two-wire energy meters is primarily aimed at low-power appliances, resulting in relatively limited measurement accuracy and range. For high-power loads, a more advanced energy meter may be required to ensure measurement accuracy.
 3. Scope of Application
3. Scope of Application
2-wire energy meters are widely used in households, small commercial establishments, and other situations where measuring the energy consumption of low-power electrical appliances is necessary. For example, they can be used to measure the energy consumption of light sources (such as bulbs, LED lights, etc.), as well as personal household appliances (such as televisions, refrigerators, washing machines, etc.). Additionally, 2-wire energy meters are also commonly used in industrial automation control systems for sensors and instruments to achieve remote monitoring and data collection.
4. Wiring method
When wiring, it is essential to ensure that the two terminals of the two-wire energy meter are correctly connected to the power supply and the load. Generally, one terminal connects to the live wire (phase wire) of the power supply, while the other terminal connects to the load. It is important to note that since the two-wire energy meter does not have a neutral wire connection, it is necessary to ensure that other devices or components in the circuit (such as switches, sockets, etc.) also comply with the requirements of the two-wire system.
5. Precautions
a. Choose the appropriate energy meter: When selecting a two-wire energy meter, it is necessary to choose the suitable model and specifications based on the actual load power and measurement requirements. Ensure that the measurement range and accuracy of the energy meter can meet the requirements of practical applications.
b. Correct Wiring: When wiring, it is essential to strictly follow the wiring instructions of the two-wire energy meter to ensure that the connections are correct, secure, and reliable. Avoid wiring errors or poor contacts that could result in circuit faults or measurement errors.
c. Regular Calibration: To ensure the measurement accuracy of secondary energy meters, it is necessary to regularly calibrate and verify them. The calibration cycle should be reasonably set based on the usage environment and changes in load.
d. Safety Protection: When using secondary energy meters, it is important to pay attention to safety protection measures. For example, avoid using energy meters in damp, high-temperature, or flammable and explosive environments; during wiring and maintenance, it is necessary to disconnect the power supply and take appropriate safety protection measures.

6. Conclusion
The 2-wire energy meter, as a common energy measurement device, has advantages such as simple wiring, low cost, and easy maintenance. It is widely used in households and small commercial places where measuring the energy consumption of low-power electrical appliances is necessary. However, due to the relatively limited measurement accuracy and range of the 2-wire energy meter, it is essential to make a reasonable choice based on the actual load power and measurement requirements during selection and use. Additionally, strict adherence to relevant regulations and operating procedures is required in wiring, calibration, and safety protection to ensure the normal operation and measurement accuracy of the 2-wire energy meter. However, due to the relatively limited measurement accuracy and range of the 2-wire energy meter, it is essential to make a reasonable choice based on the actual load power and measurement requirements during selection and use. Additionally, strict adherence to relevant regulations and operating procedures is required in wiring, calibration, and safety protection to ensure the normal operation and measurement accuracy of the 2-wire energy meter.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体





.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)

.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)



