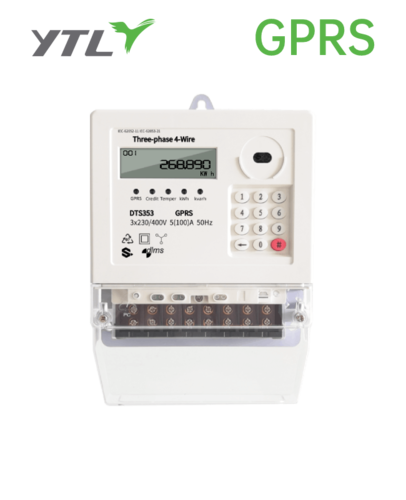
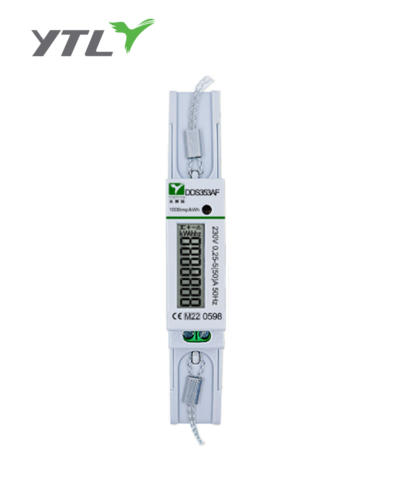
Electronic Power meter:
An Electronic Power meter, also known as an Electronic Power meter or energy meter, is a device that measures the consumption of electricity by a household or commercial establishment. The meter measures the amount of electricity used over a specific period, usually in units of kilowatt-hours (kWh). The meter provides accurate and reliable measurements of electricity consumption, which is essential for billing and energy management.
AMI (Advanced Metering Infrastructure) System:
AMI (Advanced Metering Infrastructure) is a smart grid technology that enables the communication between Electronic Power meters and the utility company's infrastructure. The system allows for real-time monitoring of electricity consumption, enabling utilities to manage energy distribution more efficiently and accurately.
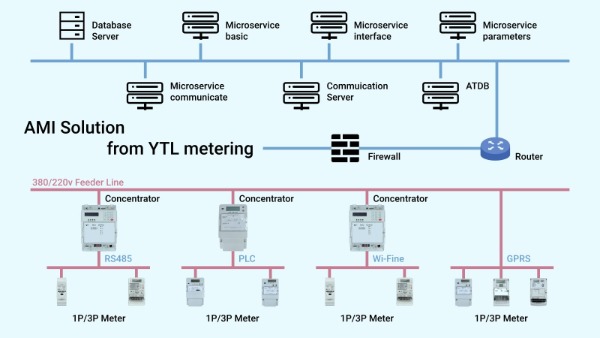
The AMI system typically consists of:
1. Smart meters: Advanced meters that can communicate with the utility company's infrastructure, providing real-time data on electricity consumption.
2. Communication networks: Cellular, wireless, or power line communication networks that enable data transmission between smart meters and the utility company.
3. Data management systems: Systems that collect, store, and analyze data from smart meters, providing insights into energy consumption patterns.
4. Utility software: Software that enables utilities to manage energy distribution, billing, and customer service.
AMR (Automated Meter Reading) System:
AMR (Automated Meter Reading) is an earlier technology that allows utilities to remotely read Electronic Power meters using various methods, such as:
1. Radio Frequency (RF) signals: Meters send RF signals to a collector device, which records the data.
2. Power Line Carrier (PLC) signals: Meters transmit data over the power grid using PLC signals.
3. Cellular networks: Meters use cellular networks to send data to the utility company.
The AMR system typically consists of:
1. Metering devices: Electronic Power meters that can transmit data wirelessly.
2. Collector devices: Devices that receive and record data from meters.
3. Data management systems: Systems that collect, store, and analyze data from meters.
Key differences between AMI and AMR systems:
* AMI systems are more advanced and provide real-time data, while AMR systems are more basic and provide periodic readings.
* AMI systems require a communication network to transmit data, while AMR systems use various methods to transmit data.
* AMI systems are more secure and provide better data accuracy than AMR systems.
In summary, both AMI and AMR systems are designed to improve the efficiency and accuracy of Electronic Power meter reading and billing. However, AMI systems are more advanced and provide real-time data, while AMR systems are more basic and provide periodic readings.


 English
English 简体中文
简体中文






.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)







