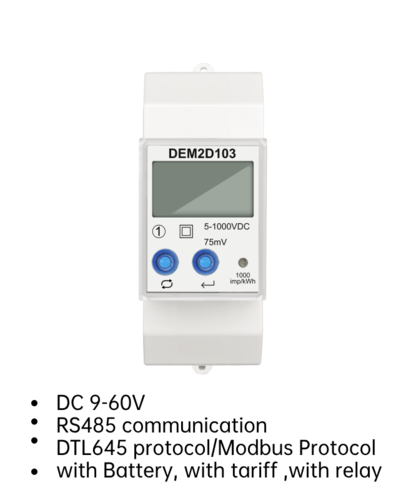
As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly popular, the infrastructure to support their charging needs is evolving rapidly. One crucial component of this infrastructure is the EV charging electricity meter. This device plays a significant role in monitoring and managing the energy consumption of EVs. Here, we explore the various benefits of using an EV charging electricity meter.
1. Accurate Measurement of Electricity Usage
One of the primary benefits of an EV charging electricity meter is its ability to provide accurate measurements of the electricity used during charging. This precision is essential for both EV owners and charging station operators. For owners, it ensures they are only paying for the actual energy consumed. For operators, it allows for precise billing and energy management.
2. Cost Savings
By monitoring electricity usage closely, EV owners can make informed decisions about their charging habits. For instance, charging during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower can lead to significant cost savings. Additionally, some electricity meters can integrate with smart home systems, enabling automated charging during the most cost-effective times.
3. Enhanced Energy Management
EV charging electricity meters provide valuable data that can be used to manage energy consumption more effectively. For example, they can help identify peak usage times and allow for adjustments to avoid overloading the electrical grid. This capability is particularly beneficial for businesses with multiple charging stations, as it helps optimize energy distribution and reduce operational costs.
4. Better Understanding of Charging Patterns
Understanding charging patterns is crucial for improving the efficiency and convenience of EV charging. Electricity meters collect data on when and how long vehicles are charged, offering insights into user behavior. This information can be used to improve the placement and availability of charging stations, enhancing the overall user experience.
5. Support for Renewable Energy Integration
As the push for renewable energy sources grows, integrating them with EV charging systems becomes increasingly important. EV charging electricity meters can facilitate this integration by providing detailed data on energy consumption and generation. This data can be used to optimize the use of renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, making EV charging more sustainable.
6. Facilitates Government Incentives and Rebates
Many governments offer incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of EVs and the installation of charging infrastructure. Accurate measurement of electricity usage through an EV charging electricity meter can help users qualify for these incentives. By providing verifiable data on energy consumption, these meters ensure that users can take full advantage of available programs.
7. Enhanced Billing Accuracy
For commercial charging stations, accurate billing is essential. An EV charging electricity meter ensures that customers are billed correctly for the energy they use. This accuracy helps build trust and satisfaction among users, as they can be confident that they are being charged fairly.
8. Improved Maintenance and Diagnostics
Modern EV charging electricity meters often come with advanced diagnostic features. They can monitor the health of the charging equipment and detect potential issues before they become serious problems. This proactive approach to maintenance can reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of the charging infrastructure.
9. Compliance with Regulations
Many regions have specific regulations regarding the measurement and billing of electricity used for EV charging. Using a certified EV charging electricity meter ensures compliance with these regulations, helping avoid potential legal issues and fines.
10. Contribution to a Smarter Grid
The data collected by EV charging electricity meters can be used to enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of the electrical grid. By providing insights into energy consumption patterns, these meters help grid operators manage demand more effectively, contributing to the development of a smarter, more resilient grid.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)