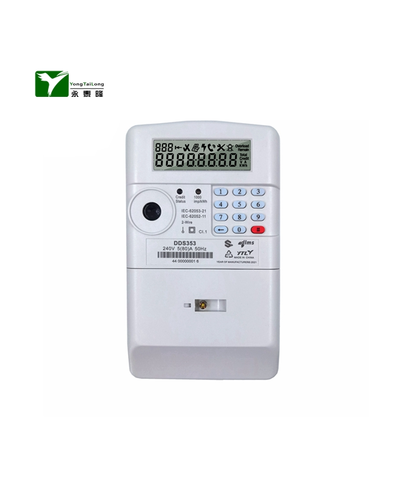
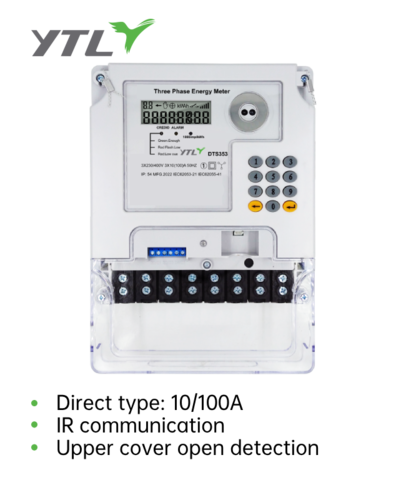
The differences between smart meters and ordinary meters are significant in several aspects, which are detailed below:
 I. Functional differences
I. Functional differences
1. Electric energy measurement function:
Ordinary meters: only have electric energy measurement function, used to record user consumption.
Smart meters: in addition to basic electric energy measurement function, also have remote meter reading, data storage, time-of-use metering, automatic control, electrical parameter measurement, and electrical information security protection functions.
2. Bi-directional measurement function:
Ordinary meters: can only measure electricity consumption in one direction.
Smart meters: add bi-directional measurement function, calculating active and reactive power consumption, as well as peak and valley metering functions.
3. Monitoring and management function:
Ordinary meters: do not have electrical monitoring and metering information management functions.
Smart meters: add electrical monitoring, metering information management, and electrical information management functions, allowing users to easily manage their electricity usage.
II. Performance differences
1. Precision and stability:
Ordinary meters: have relatively low precision and stability, affected by environmental factors.
Smart meters: adopt advanced electronic and communication technologies, having higher precision and stability, able to work normally in complex environments.
2. Anti-interference capability:
Ordinary meters: have relatively weak anti-interference capabilities, easily affected by external factors.
Smart meters: have stronger anti-interference capabilities, ensuring data accuracy and reliability.
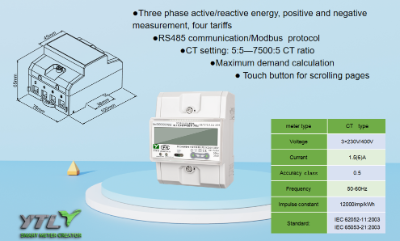 III. Usage differences
III. Usage differences
1. Meter reading method:
Ordinary meters: require users to periodically go to the power company to read the meter, a time-consuming and error-prone process.
Smart meters: allow remote meter reading, significantly reducing user workload and improving data accuracy and timeliness.
2. Data query and operation:
Ordinary meters: users cannot directly query or operate meter data.
Smart meters: users can query and operate data through mobile apps or computers, enabling real-time monitoring of electricity usage anywhere, anytime.
IV. Other features
1. Real-time monitoring and data collection:
Smart meters use real-time monitoring technology to monitor power load, current, voltage, etc., providing users with more detailed electricity usage information.
2. Multiple billing modes:
Smart meters have multiple billing modes, such as time-of-use billing, tiered billing, peak-valley billing, etc., meeting the diverse electricity needs of users.
3. Alarm function:
Smart meters can set alarm functions for overcurrent, overload, short circuit, etc., timely detecting abnormal situations and notifying users and the power company, improving power supply safety.
In summary, smart meters surpass ordinary meters in functionality, performance, and usage methods, better meeting user needs and improving power supply efficiency and safety.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体


.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)


.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)







