In the realm of modern electrical systems, the pivotal role of multi-function power meter cannot be overstated. These sophisticated devices serve as the linchpin in monitoring, measuring, and managing electrical power in diverse applications, ranging from industrial settings to commercial enterprises. To delve into the intricate workings of multi-function power meter, it is imperative to dissect their fundamental components and operational principles.
In the realm of modern electrical systems, the pivotal role of multi-function power meter cannot be overstated. These sophisticated devices serve as the linchpin in monitoring, measuring, and managing electrical power in diverse applications, ranging from industrial settings to commercial enterprises. To delve into the intricate workings of multi-function power meter, it is imperative to dissect their fundamental components and operational principles.
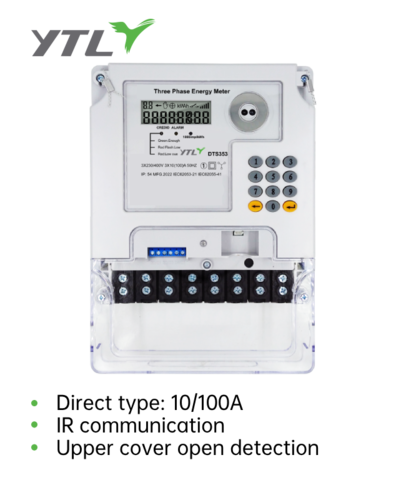
At its core, a multi-function power meter is designed to provide comprehensive insights into the electrical parameters of a system. These parameters include voltage, current, power factor, frequency, and energy consumption, as well as other factors. The meter's ability to simultaneously measure and display these variables makes it an indispensable tool for engineers, electricians, and facility managers who are seeking to optimize power efficiency and maintain operational integrity.
One of the primary components of a multi-function power meter is its sensor array. Advanced sensors, such as Hall effect sensors and current transformers, are used to accurately measure the current flowing through a circuit. Voltage sensors, which are often based on capacitive or electromagnetic principles, are used to measure the voltage across a system. These sensors work together to provide real-time data, which forms the basis of the meter's operation.
The heart of the multi-function power meter lies in its microprocessor, a sophisticated brain that processes the data acquired from the sensors. This microprocessor employs complex algorithms to calculate various electrical parameters, ensuring precision and reliability in the readings displayed. Moreover, it facilitates communication with other devices and systems, enabling seamless integration into larger control and monitoring networks.
A distinctive feature of multi-function power meter is their ability to measure power quality parameters. Harmonics, voltage sags, swells, and transients are meticulously analyzed by the meter to assess the overall health of the electrical system. This capability is pivotal in preventing equipment damage, enhancing the longevity of machinery, and maintaining a stable power supply.
Furthermore, multi-function power meter often incorporate communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, or Ethernet, allowing for remote monitoring and control. This connectivity is instrumental in the era of smart grids and Industry 4. 0, as it empowers users to access real-time data, make informed decisions, and implement corrective measures promptly.
Another noteworthy aspect of these meters is their role in energy management. By continuously monitoring energy consumption patterns, users can identify inefficiencies, allocate resources judiciously, and implement energy-saving measures. This not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with the global imperative of sustainable energy practices.
In conclusion, the functionality of multi-function power meter is a testament to the advancements in electrical engineering and technology. From sensor precision to microprocessor intelligence, these devices epitomize the synergy between hardware and software in the pursuit of efficient power management. As our reliance on electrical systems continues to grow, the role of multi-function power meter will remain crucial in fostering a resilient, sustainable, and technologically advanced future.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体