A master-slave (or parent-child) DC energy meter is a specialized type of energy measurement device used in direct current (DC) applications. This setup involves a master meter that communicates with one or more slave meters to measure and monitor energy consumption across multiple circuits or systems. The master meter typically collects data from the slave meters, consolidating the information for analysis and management. Below are the main features and working principles of master-slave DC energy meters:
Main Features
1. Hierarchical Structure: The system consists of a master meter and multiple slave meters. The master meter serves as the central unit, while the slave meters operate under its control.
2. Centralized Monitoring: The master meter aggregates data from all connected slave meters, providing a comprehensive overview of energy consumption across multiple circuits.
3. Real-time Data Collection: The master meter can access real-time data from slave meters, enabling prompt monitoring and fault detection.
4. Data Logging and Reporting: Master-slave systems often have data logging capabilities, allowing for historical data storage and generating reports for energy consumption analysis.
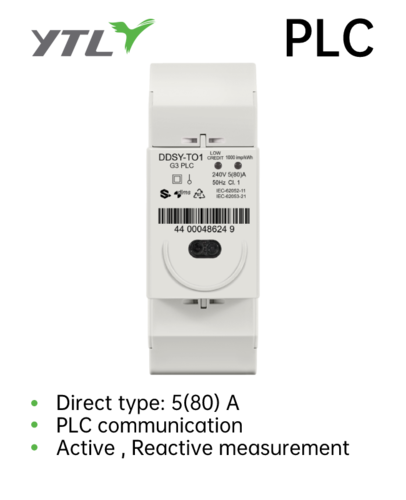
5. Communication Protocols: These systems typically support various communication protocols (e.g., RS485, Modbus), facilitating data transfer between meters and external monitoring systems.
Working Principle
The operation of a master-slave DC energy meter system involves the following key steps:
1. Data Collection: Each slave meter measures the current and voltage of its respective circuit. The slave meters send this data to the master meter for processing.
2. Power Calculation: The master meter calculates the power consumption based on the data received from each slave meter, using the formula \(P = U \times I\).
3. Energy Integration: The master meter integrates the power readings over time to compute the total energy consumption for each circuit, displayed in kilowatt-hours (kWh) or ampere-hours (Ah).
4. Display and Communication: The master meter displays the aggregate data and can transmit this information to external systems for further processing or monitoring.
Application Scenarios
Master-slave DC energy meters are widely used in various applications, including:
- Large-scale solar energy systems with multiple panels
- Industrial facilities with multiple DC-driven machinery
- Electric vehicle charging stations with numerous charging points
- Data centers managing multiple servers and equipment
- Energy management systems in commercial buildings
Conclusion
In summary, a master-slave DC energy meter system is an advanced solution for monitoring and managing energy consumption across multiple direct current circuits. Its hierarchical structure, real-time data capabilities, and centralized monitoring features make it an effective tool for optimizing energy use in various applications.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体







.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)




