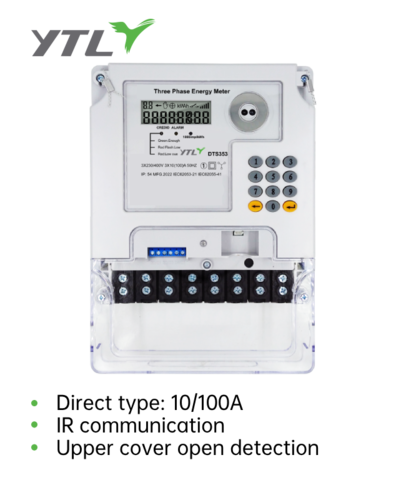
An Alternating Current electricity, which is AC electricity meter, also known as an electricity meter or a watt-hour meter, is a device used to measure the amount of electricity consumed by a household, business, or industrial facility. It measures the amount of electrical energy used in terms of kilowatt-hours (kWh).
AC electricity meter series are designed to measure the voltage and current of an alternating current (AC) electrical circuit, which is the type of electrical power used in homes and businesses. The meter measures the total amount of energy consumed by the circuit over a given period of time, usually in units of kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Here are some key features of AC electricity meter:
1. Measuring principle: AC electricity meter use a mechanical or electronic device to measure the voltage and current of the electrical circuit. The measurement is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
2. Measurement units: The meter measures energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is calculated by multiplying the voltage, current, and power factor (cos φ) of the electrical circuit.
3. Accuracy: AC electricity meter series are designed to be accurate to within 0.5% or 1% of the measured value.
4. Display: The meter displays the measured value on an analog dial or digital display, typically in units of kWh.
5. Tamper-resistance: Modern AC electricity meter series are designed to be tamper-resistant to prevent unauthorized access or manipulation.
Types of AC electricity meter:
1. Mechanical meters: These are traditional meters that use a mechanical mechanism to measure energy consumption.
2. Digital meters: These meters use electronic circuits to measure energy consumption and display the results on a digital display.
3. Smart meters: These advanced meters use wireless communication technology to transmit energy consumption data to utility companies and provide real-time monitoring.
AC electricity meter series are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to measure energy consumption and bill customers accordingly. They play a crucial role in managing energy distribution, monitoring consumption patterns, and promoting energy efficiency.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体