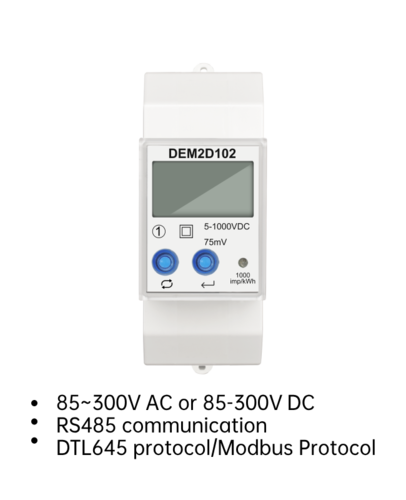
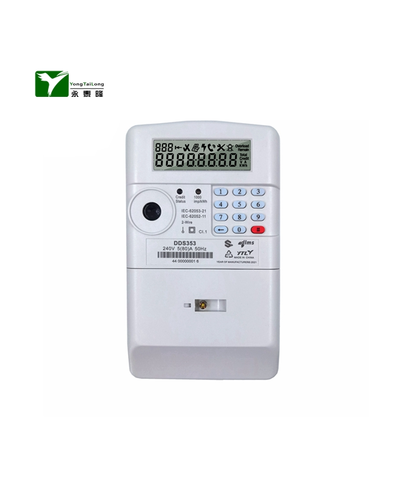
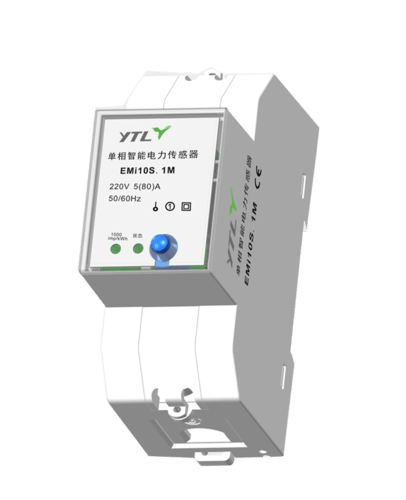
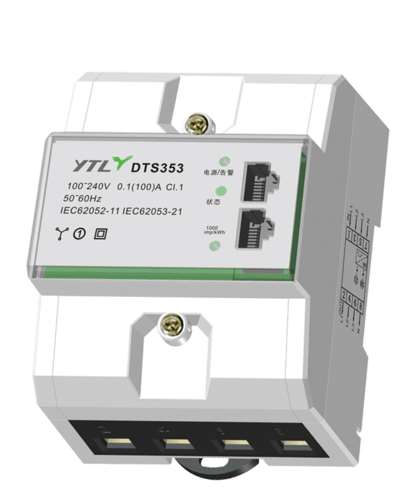
A multifunctional energy meter is a versatile instrument used for measuring electrical quantities in high and low voltage power grids. In addition to measuring active and reactive energy, it also possesses more than two functions such as time-of-use measurement and demand measurement, and is capable of displaying, storing, and outputting data.
I. Functional Characteristics
1.Measurement Function: The multifunctional energy meter is capable of measuring forward active energy, reverse active energy, and four-quadrant reactive energy. It can also perform time-of-use measurement, separately accumulating and storing total, peak, sharp, flat, and valley active and reactive energy according to the corresponding time periods.
2.Parameter Monitoring: The meter can measure, record, and display the current total and phase-specific voltage, current, power, power factor, and other operational parameters with minimal measurement error. When a parameter exceeds or falls below a set limit, it can record the event.
3.Display Function: It features a large LCD screen that can operate in two modes: automatic cycle display and button-triggered display. Besides displaying daily electricity usage data, it also shows corresponding symbols and issues an alarm prompt when an abnormality is detected in the meter.

4. Communication Function: The multifunctional energy meter comes equipped with various communication interfaces, such as RS-485 and far-infrared communication ports. It can also have built-in communication modules like NB-IOT wireless IoT, 4G wireless, or power line carrier wireless. These communication interfaces operate independently of each other without interference, ensuring the stability of data transmission.
5. Load Curve: The multifunctional energy meter can record data at set intervals, including any combination of electrical energy data items such as voltage, current, frequency, active/reactive power, power factor, and total active/reactive energy.
6. Event Recording: The energy meter can provide fault event information, enabling remote fault diagnosis. It also offers a detailed list of event records, including total reset times, total time calibration times, loss of voltage, phase failure, cover opening, power failure, power supply anomalies, and switching operations.
7. Power-off Meter Reading: In the event of a power outage, the energy meter can be awakened via button press or infrared to read data such as electrical energy.
8. Cost Control Function: The energy meter can execute commands such as switch-off and switch-on issued by the system backend. After strict password verification and security authentication, it can control the switch-off and switch-on of the energy meter to protect electricity safety.
Additionally, some multifunctional energy meters also feature three-phase voltage/current unbalance analysis, current K-factor, three-phase voltage/current total harmonic and 2~31 sub-harmonic analysis, high-precision electrical measurement and energy metering, power quality analysis (such as voltage swell/sag and interruption monitoring), SOE event recording function, big value recording, timed recording, and limit monitoring functions.

II. Product Function Applications
1. Power Measurement and Management:
Accurate Measurement: Multifunctional energy meters can precisely measure electrical parameters such as active energy, reactive energy, current, voltage, and power factor, providing accurate data support for power measurement.
Time-of-Use Measurement: Supporting time-of-use measurement, these meters can record energy consumption data for different time periods, helping users understand usage trends and optimize electricity strategies.
Billing Settlement: By interfacing with the billing systems of power companies, multifunctional energy meters can automatically calculate electricity costs, improving the efficiency and accuracy of billing settlements.
2. Electricity Monitoring and Management:
Real-Time Monitoring: Multifunctional energy meters can monitor changes in electrical parameters such as voltage and current in real-time, promptly identifying anomalies in the power grid.
Abnormality Alarms: When abnormalities such as voltage irregularities, current irregularities, or power factor irregularities are detected, the meters can issue alarm signals to alert users or management personnel for timely action.
Load Management: By analyzing electricity usage data, multifunctional energy meters can assess the load conditions of users, providing data support for load management.
3. Monitoring of New Energy Generation Systems:
Energy Generation Measurement: In new energy generation systems, multifunctional energy meters can accurately measure the amount of electricity generated, providing precise data for evaluating the economic benefits of new energy systems.
Power Quality Monitoring: They monitor the power quality of new energy generation systems, including voltage fluctuations and frequency changes, ensuring that the power quality meets national standards.
Event Recording and Analysis: These meters record various events in new energy generation systems, such as faults and shutdowns, and conduct detailed analysis to provide data support for optimizing system operations.

4. Smart Grid Construction
Data Collection and Transmission: Multifunctional energy meters can collect a large amount of electricity consumption data and transmit it to the smart grid system through communication networks, providing essential data support for the construction of smart grids.
Remote Monitoring and Control: With support for remote monitoring and control functions, these meters enable remote supervision and management of the power grid, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
Data Analysis and Decision Support: By analyzing electricity consumption data, multifunctional energy meters provide decision-making support for smart grids, assisting power companies in formulating more rational power dispatching plans.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体