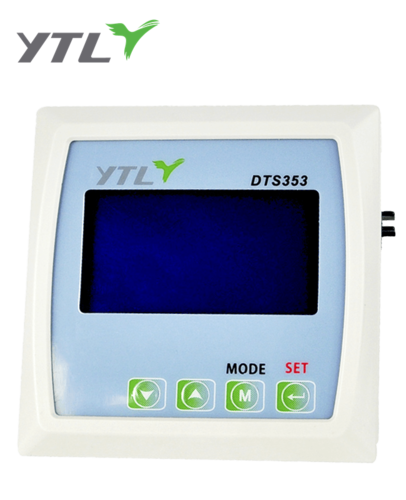
ANSI watt hour meter, also known as an electricity meter or simply a utility meter, is a device designed to measure the amount of electrical energy consumed in a building or facility. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) is responsible for setting the standards for these devices in the United States to ensure their reliability and accuracy.
The ANSI watt hour meter works by measuring the flow of electrical current through a circuit and calculating the total energy consumed over a specific period of time. Some meters operate on a monthly cycle, with readings taken at the beginning and end of each billing period. The difference between these readings represents the amount of energy used during that period.
The design of the meter varies depending on the specific application and power requirements. Residential meters typically have a lower capacity than commercial or industrial meters, which may need to measure much higher levels of electricity usage. Many modern ANSI watt hour meters utilize digital displays and advanced communication technologies to enable remote monitoring and control.
In addition to accurately measuring energy consumption, ANSI watt hour meters also play a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical grid. Utilities use these meters to monitor power usage and detect potential problems, such as circuit overloads or other electrical faults, that could result in power outages or equipment damage.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is a rapidly evolving technology that is transforming the way utilities manage their electricity networks. This includes the deployment of smart meters, which are capable of providing detailed real-time data on energy usage and other key metrics. AMI systems also allow utilities to remotely control and optimize power delivery, which reduces costs and improves efficiency.
Despite the benefits of modern metering technology, there are also concerns about privacy and security. Smart meters and AMI systems may collect sensitive data about energy usage and other user information, raising questions about how this data is stored, used, and protected. Utilities must balance the benefits of these advances with the need to respect user privacy and safeguard against cyber threats and other security risks.
In conclusion, an ANSI watt hour meter is a critical component of the modern electrical grid, responsible for measuring energy consumption and maintaining the safety and reliability of the system. As technology continues to evolve, the role of these devices will only become more important, enabling utilities to better control and optimize power delivery for the benefit of all users.
Knowledge
What Is an ANSI Watt Hour Meter?

YTL is a professional supplier of energy meter and AMI solution. the Top 100-enterprise with most investment value in Zhejiang. And“Yongtailong”is the famous brand of Zhejiang. With nearly 20 years' experience in energy metering, we devote ourselves to providing competitive projects and creating value for customers.
● Online + Offline. Provide cost-effectiv solutions
● Strict quality control mechanism.High quality assurance
● Five R&D centers,combine with hardware&software design, experiment and testing
● Global service capability, provide customers timely and effective solution
● Good customer feedback. Reliable after-sales service
● Online + Offline. Provide cost-effectiv solutions
● Strict quality control mechanism.High quality assurance
● Five R&D centers,combine with hardware&software design, experiment and testing
● Global service capability, provide customers timely and effective solution
● Good customer feedback. Reliable after-sales service
-
- ABOUT YTL
- About YTL
- Factory
- Honor
- Development
- Privacy
-
- YTL culture
- Culture
- Values
- Advantage
- Three Phase kWh Meter
-
- products
- Single Phase Din Rail Meter
- Three Phase Smart APS Electric Energy Meters
- Three Phase Multi Function Electronic Energy Meter
- Digital Electric Meters
- Electronic Energy Meter
- Electronic Energy Meters
- Three Phase Keypad split type Energy Meter
- Single Phase IC Card Prepayment Energy Meters
- Three Phase Anti-tamper Suspension Energy Meters
-
- Information Activity
- Exhibition News
- Blog
- Staff Activity
- Single Phase Smart Watt Hour Meter
COPYRIGHT © 2020 Zhejiang Yongtailong Electronic Co., Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED .  China Electronic Energy Meters Manufacturers
China Electronic Energy Meters Manufacturers

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体

.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)