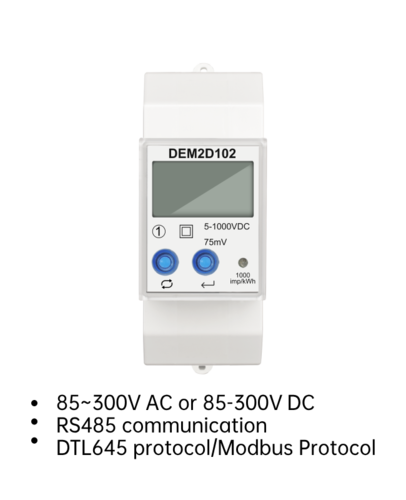
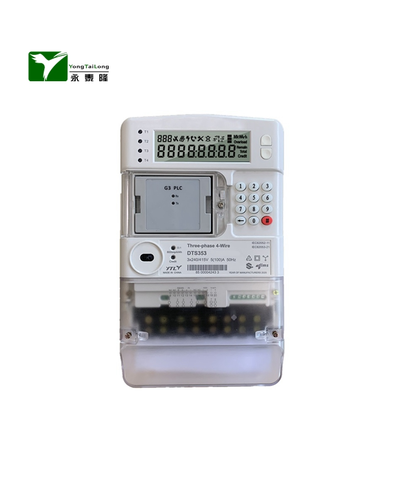
An electric meter, also known as an electricity meter, is a device that measures the amount of electricity used by a household, business, or industrial facility. Its primary function is to track and record the amount of electricity consumed over a specific period, usually in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
The electric meter is typically installed at the point of supply, which is usually the main electrical service entrance of a building. It measures the electrical energy consumed by monitoring the flow of electricity through a current transformer and a voltage transformer. The meter then converts this data into a readable format, usually in units of kWh.
There are different types of electric meters, including:
1. Analog meters: These are traditional meters that use mechanical dials and pointers to display the amount of electricity consumed.
2. Digital meters: These meters use electronic displays and can provide more accurate and detailed readings.
3. Smart meters: These advanced meters use wireless technology to transmit consumption data to utility companies in real-time, enabling remote monitoring and automated billing.
The benefits of electric meters include:
1. Accurate billing: Electric meters ensure accurate measurement of electricity consumption, which helps utility companies to bill customers correctly.
2. Energy efficiency: By monitoring consumption patterns, households and businesses can identify areas for energy savings and optimize their usage.
3. Grid management: Electric meters help utilities to manage energy distribution and demand more effectively, reducing the risk of power outages and brownouts.
4. Real-time data: Smart meters provide real-time data on energy consumption, enabling utilities to respond quickly to changes in demand and optimize energy distribution.
Overall, electric meters play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and reliable delivery of electricity to consumers while also helping to promote energy conservation and sustainability.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体


.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)




.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)


.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)


