Basic knowledge of electric energy meter
1.The basic parameters of the electric energy meter
- Voltage
Generally, electric meters are divided into two voltages: 220V (230V) and 110V (120V). The voltage of special high-voltage meters is 57.7V. Different voltages need to consider whether the power supply can work, whether the high voltage exceeds the standard, and whether the low voltage can output stably.
- Current
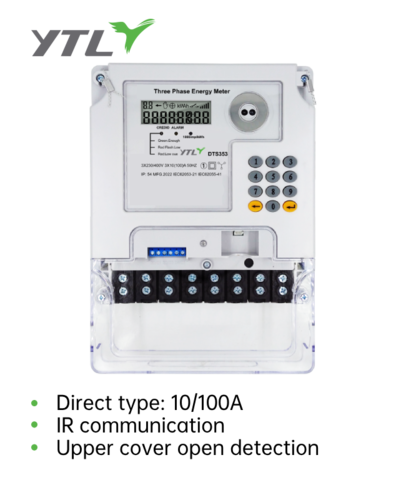
Direct type: 5(100)A, 10(100)A, 5(60)A…
Mutual inductance: 5(10)A, 1.5(6)A, 1(10)A…
- Constant
Direct type: 800imp/kWh, 1600imp/kWh, 3200imp/kWh, 6400imp/kWh
Mutual inductance type: 8000imp/kWh, 10000imp/kWh, 12000imp/kWh, 12800imp/kWh
The constant represents the amount of energy represented by each pulse. It can also be said that how many pulse signals are needed for one kilowatt of electricity. A large CT needs to be connected to the outside of a mutual inductance meter, and the actual input current is much smaller than the primary current.
- Frequency
50Hz and 60Hz general electric meters can be compatible with two frequencies.
- Accuracy class
Normal level: 0.2S 0.5S 1.0 2.0 level Used to measure electric energy.
At present, Yongtailong mainly produces level 1 meters and some 0.5 level meters; precision level: 0.01 level 0.05, which is mainly used as the calibration benchmark for calibrating ordinary-level electric energy meters.
- basic functions of the electric meter
- Electricity Metering
Electric energy measurement is generally divided into active power: forward active power, reverse active power; reactive power: forward reactive power, reverse reactive power, four-quadrant reactive power.
- Demand
Generally, demand divided into max demand measure, each month max demand measure,cumulative demand, continuous cumulative demand.
The demand can be understood as the average power over a period of time, which represents the user's short-term high-power demand, and is used to analyze the user's maximum load.
- Tou
Timetable: The day is divided into different time periods, with different charging prices.
Time zone table (season table): The year is divided into different time zones, and different time zones can be selected.
Public holiday: A specific timetable is used on a specific day of the year.
- Event
Events generally include: opening the cover, loss of voltage, power failure, setting parameters, reverse, over voltage, under voltage, over current, etc. The event records can be stored individually or in pairs, and the occurrence and recovery events are recorded at the same time.
- Communication
RS485 ,Twisted pair communication requires wiring and the maximum distance is 1200 meters.
IR, Local infrared communication, one-to-one communication.
- BUS, Two-wire communication can provide power.
RF, Point-to-point wireless communication to realize short-distance wireless communication.
WIFI, Join the wireless hotspot to realize remote communication.
LORA, Spread spectrum wireless technology has relatively better communication distance.
LORAWAN, Wireless communication with a fixed base station.
ZIGBEE, 2.4G frequency band wireless communication, using zigbee physical layer, can realize routing and forwarding.
GPRS/3G/4G, The communication in the cellular network can realize remote reading and access to the operator's network.
PLC(Narrowband, broadband): Current line carrier communication, using existing power grid lines to realize data communication.
NB-IOT, Narrowband IoT has more access points and better penetration.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体
-1.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)








.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)


